Submit your email address to get a link for quick download on your desktop and get started!
You might need to access serial ports from within a VMware virtual machine either for configuration, logging communication, or debugging purposes. It’s easy to add new serial ports, both physical and remote, in VMware Workstation Pro as long as you meet the prerequisites.

However, accessing them for later use within the virtual environment is another matter. And that’s where the Serial Port Redirection tool comes into the picture.
In this post, we’ll show you how to add a serial port in VMware virtual machines, explain the different connection types, and demonstrate how to access it in a VM. Adding a Serial Port to a Virtual Machine.
Adding a serial port (or COM port) to a virtual machine (VM) allows you to interact with serial devices like routers or development boards within the VM environment. There are many ways you can connect a virtual serial port, including connecting to a physical port, file, named pipe, and network.
Virtual machines can have a maximum of 32 COM ports. However, when creating a VM, you can actually choose not to include any at all. If you choose that approach, the guest operating system (the OS running inside the VM) simply won't see any available serial ports.
Before adding a virtual serial port, ensure that your virtual machine is turned off already.
Make sure that you’re aware of the right media types and vSPC connection details relevant to your port configuration. You also need to grant a “Virtual Machine .Configuration.Add or Remove Device” privilege to continue.
Specific connection types have unique prerequisites, too. For example, the following firewall rule sets are needed if you want to use your serial port over a network:
With that established, here’s how you configure a VMware virtual serial port.
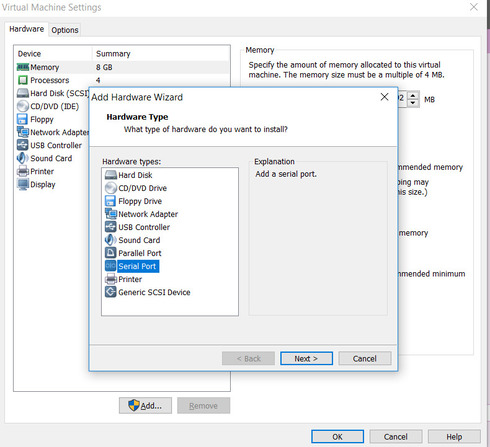
Depending on what kind of data processing you want to achieve, you need to select a particular connection type for your virtual serial port. Here’s a quick breakdown of the four different connection methods you can use:
If you selected a named pipe connection in the “New Serial port” drop-down menu, click the “Pipe Name” field and type your preferred name (e.g., “\\.\pipe\namedpipe”).
You can simply use the default name provided if you’re using a Windows host computer. Just make sure that you use the same name on both the server and the client.
Then, from the drop-downs available, choose “Near end” and “Far end” of the pipe.
If you choose a network connection type, you can also select whether to set up your serial port for a client or server connection.
If you opt for a server connection, you gain control over the virtual machine connected to your serial port. It makes your VM act like a server, waiting for an incoming connection from your host. This is ideal for scenarios where you want occasional control over the VM, like during debugging or configuration.
Meanwhile, choose a client connection if you want to use your virtual machine as the client. In other words, the VM actively initiates the connection to a designated program upon startup. It’s common for logging applications where you automatically send data to another system.
To configure your VM with a serial port server connection with a telnet://:11111 URI (Uniform Resource Identifier), run the following command.
telnet yourESXiServerIPAddress 11111Meanwhile, you can also set up your serial port using a client connection by running the Telnet Server on Linux on port 11 (telnet://yourLinuxBox:11). Use the following command.
telnet://yourLinuxBox:11
Virtual serial ports are handy when it comes to debugging or logging purposes. They’re easy to add via VMware Workstation Pro, but accessing them inside the virtual environment is still done most easily with Serial to Ethernet Connector.
SEC for Windows
SEC for Linux